Important Car Sensors and Their Purpose in the Workings of Your Engine
Modern car engines have come a long way since their humble beginnings, and while most are still fuel-injected, they do contain a fair amount of electronics and sensors that provide important information to the electronic control unit in order to ensure the engine works optimally. One such important sensor is the manifold absolute pressure sensor, also known as the MAP sensor.
Contents
What is a MAP Sensor?
MAP sensors ( manifold absolute pressure sensors) are one of several sensors used to measure various parameters in an engine’s exhaust gas flow. It works by sending a signal to the ECU that corresponds to the pressure in the manifold of an engine. The ECU then uses this information to determine how much fuel should be injected, which in turn affects how much oxygen is present in order to produce optimal power and efficiency.
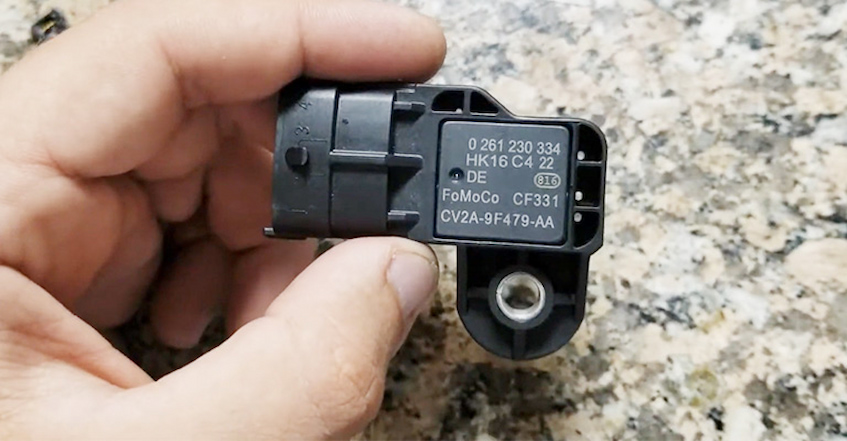

The MAP sensor is one of several sensors that work together to control the amount of fuel being delivered. Other sensors include things like exhaust temperature, coolant temperature and throttle position, air intake and oxygen sensors.
Where is it Located?
In most cases, the MAP sensor is located on the intake manifold and is connected to a wire that runs from it to the ECU. The MAP sensor itself consists of two parts: a plastic housing with a metal diaphragm inside and a potentiometer (variable resistive element). When pressure changes in the exhaust gas flow cause the diaphragm to move, the change in voltage across the potentiometer is measured by an analogue-to-digital converter in the ECU.
The location of the MAP sensor varies depending on the make and model of your vehicle, although it’s generally located near other sensors such as the coolant temperature sensor or throttle position sensor. Now, let’s talk about the purpose of the coolant temperature and throttle position sensors.
What is a Throttle Position Sensor?
The throttle position sensor (TPS) is another important sensor used by modern engines, as it measures the position of the throttle and sends a signal to the ECU that indicates how far open or closed it is. The ECU uses this information to determine what type of fuel injection strategy should be employed in order to provide maximum power and efficiency. In some cases, the TPS can also help with idle stability control.
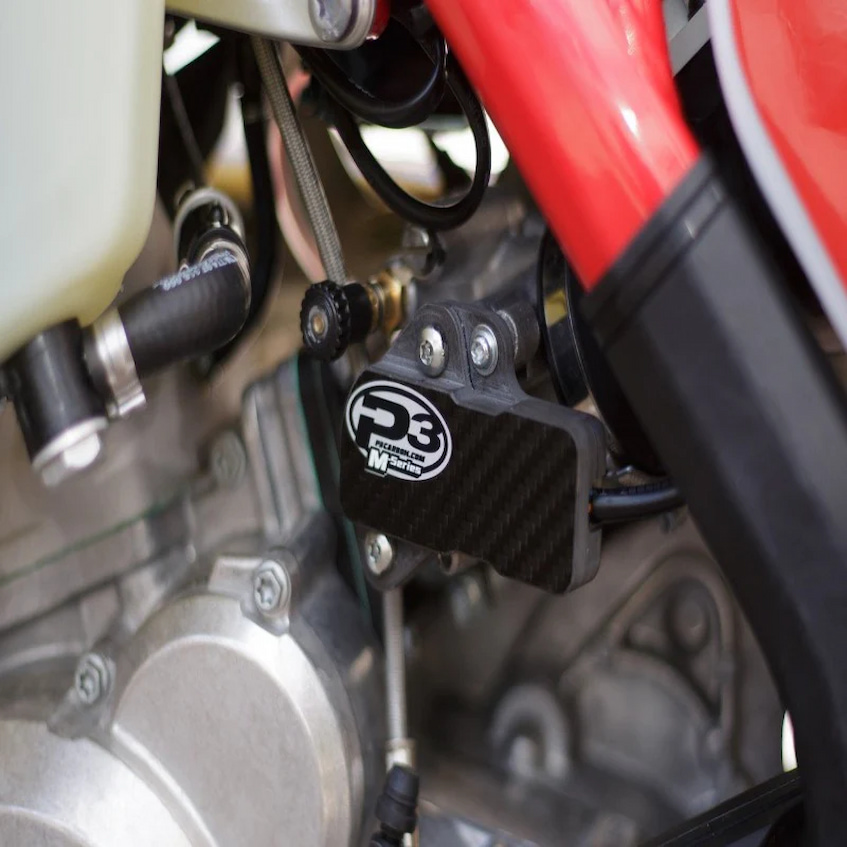

As you may have guessed, the throttle position sensor is located on the throttle body of an engine. It consists of a metal housing and two wires that run from it to the ECU. The position of the throttle is determined by a potentiometer (variable resistive element) inside the sensor itself.
What is Coolant Temperature Sensor?
Coolant temperature is another important parameter used in modern car engines, especially when it comes to fuel injection strategy. By knowing how hot the coolant is, the ECU can determine how much fuel should be injected and at what time. The coolant temperature sensor (CTS) works by sending a signal to the ECU that corresponds to the temperature of the engine’s coolant.
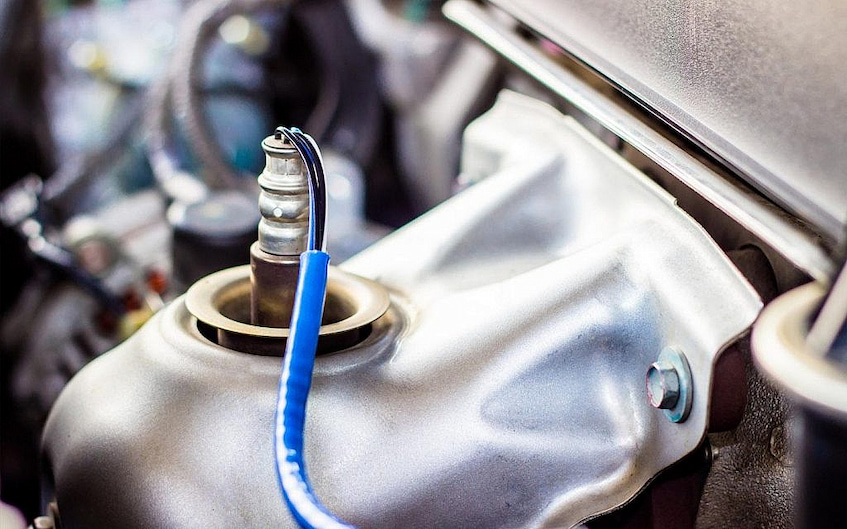
What is an Oxygen Sensor?
The oxygen sensor (O2) measures the amount of unburnt oxygen in the exhaust gas and sends a signal to the ECU that indicates how much unburnt fuel there is present in the mixture. This information can be used by the ECU to determine whether or not more fuel should be injected into the engine, as well as how much power can be produced before too much unburnt fuel is present.
The oxygen sensor itself consists of a wire that runs from it to the ECU and a metal housing containing two electrodes, one of which is made from platinum. The exhaust gas passing through the oxygen sensor reacts with the platinum electrode and changes its electrical properties in relation to the amount of unburnt fuel present in the mixture.

Conclusion
As you can see, there are several sensors that work together to provide important information to the ECU in order to determine the optimal fueling strategy. If any one of these sensors fails, it could result in poor performance and inefficient fuel economy. You can find a wide range of replacement manifold absolute pressure sensors, as well as all other sensors online or at your local car parts dealership. All you have to do is find a sensor that’s compatible with your vehicle, and if you’re not sure which one it is then consult a professional mechanic.
Installation should be done by a professional mechanic, as improper installation can lead to further problems with your car’s engine. In addition, some sensors require special tools or expertise in order to be installed properly.
If you’re not sure how to replace a sensor, then consult a professional mechanic. It’s always better safe than sorry when it comes to replacing these important components that help keep your car running at optimal efficiency.


No Comments